Basic Functions of the Suspension System
1-Ride Comfort: Isolates the vehicle and passengers from road inputs.
2-Improved Road Holding: Ensures continuous contact between the tire and road for better traction, braking, steering, and stability.
3-Handling: Positions the tires correctly for easier steering and improves the vehicle’s driving characteristics.
Key Components
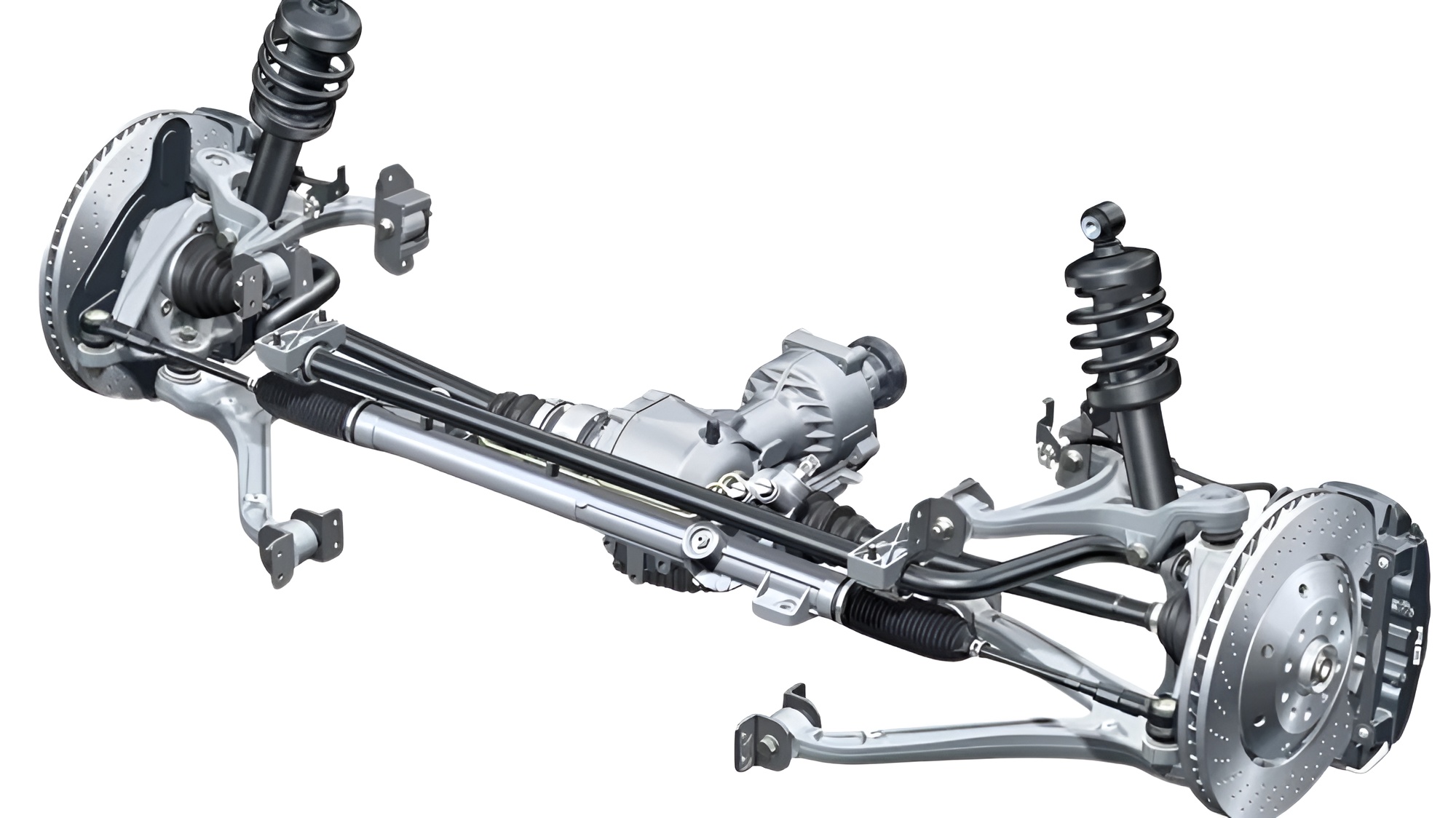

Control Arms and Track Control Arm
They determine the kinematics of the wheel relative to the chassis, setting the limits and manner in which the wheel moves.
Axle Knuckle
This is the part where the wheel, brake, and steering systems are attached.
Ball Joint
The connection mechanism between the axle knuckle and the control arms.
Rubber Bushings
These are additional units that absorb vibrations and are located at the connection points
What is Control Arm?
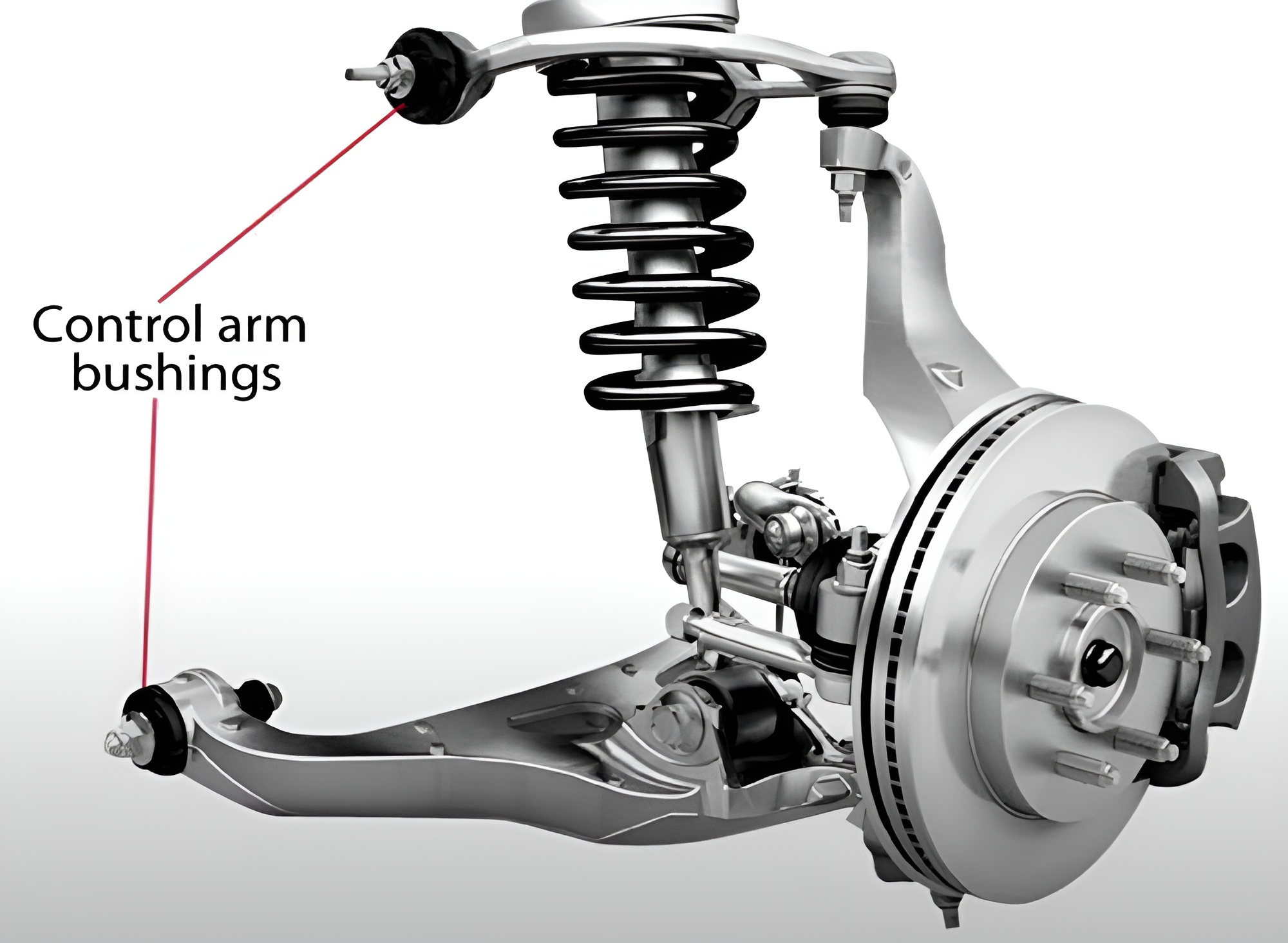
Control arm is a suspension component that connects the vehicle’s chassis to the wheel assembly, working under constant dynamic and static loads. The control arm prevents the wheel from moving forward, backward, or side-to-side and it absorbs vibrations and sudden impacts from the road through bushings and a ball joint that connects it to the wheel. Control arms are crucial for driving safety and comfort, with different types such as L-shaped, I-shaped, and V-shaped geometries. They can be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum, and cast iron.
Control Arm Failure Symptoms
Control arm failure can manifest in various ways, with most issues originating from ball joint failures. A completely failed ball joint can lead to a disconnection of the steering knuckle, causing a loss of vehicle control. Control arm bushings can also wear out and fail, resulting in clunking noises, steering instability, and loss of control. Here are the key symptoms:
1.Clunking Noise
One of the earliest signs of a faulty control arm is a clunking noise when driving over uneven road surfaces. You may also hear a clunking sound when accelerating or decelerating, but it’s most noticeable when driving over bumps or speed bumps at lower speeds. This could indicate a failing ball joint or possibly worn-out bushings.
2.Steering Instability
Another symptom that could indicate control arm issues is unsteady steering. This is common with faulty bushings that have caused the alignment to go off, leading to the vehicle pulling to one side when the driver hits a bump. This problem, known as “bump steer,” becomes more pronounced when driving on rough or uneven terrain. It could also indicate that your idle arm or steering linkages are in poor condition, so ensure these components are inspected during troubleshooting.Persistent vibration throughout the vehicle could also be a sign that the control arm is beginning to fail. However, this isn’t the only possible cause. Given that the control arm absorbs most of the energy and serves as the connection between the suspension and chassis, other issues such as unbalanced tires or faulty steering components could exacerbate the problem, especially if your control arm is already compromised.
3.Uneven Tire Wear
Uneven tire wear can also be a potential sign of a faulty control arm, as it suggests issues with alignment. As control arm bushings wear out, they can cause misalignment in the vehicle, leading to excessive wear on the inner or outer edges of the tire. While this may sometimes only indicate the need for a proper alignment, it could also stem from worn bushings.

Actions to Take for Control Arm Failures
When control arm failures are detected, a series of steps should be followed to address the issue and prevent further damage. Here are the necessary actions to take:
1.Visual and Physical Inspection:
First, conduct a visual and physical inspection of the control arm and its associated components. Check for wear, cracks, or deformation in the ball joints, bushings, and connection points.
2.Part Replacement:
Once faulty parts are identified, they should be replaced. Control arm bushings, ball joints, and other connecting components should be renewed as necessary, following the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations and considering the parts’ service life.
3.Alignment Check:
After replacing any parts, it is crucial to check the vehicle’s wheel alignment. Uneven tire wear may indicate alignment issues, so a professional alignment service should be performed.
4.Suspension System Inspection:
Control arm failures often affect other components of the suspension system. Therefore, inspect the condition of the shock absorbers, springs, and other suspension elements.
5.Regular Maintenance:
Regular inspection and maintenance of the control arm and suspension system components help prevent potential failures. Maintenance should be carried out according to the maintenance intervals specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
Tests Used for Control Arms
Various tests are conducted to evaluate the strength and performance of control arms. Here are some common test methods:
1.Dynamic Load Test:
This test is performed to assess how the control arms perform under dynamic loads. The durability and flexibility of the control arm are measured while the vehicle is in motion.
2.Static Load Test:
This test is used to examine how control arms respond to static loads. A fixed load is applied to measure the deformation and durability of the control arm.
3.Fatigue Test:
This test determines how durable control arms are under prolonged use. Continuous and repetitive loads are applied to evaluate the control arm’s lifespan and performance.
4.Material Tests:
Various material tests are conducted to determine the quality and durability of the materials used in control arms. Tests such as tensile testing, hardness testing, and corrosion testing are used to evaluate material performance.
5.Ball Joint Test:
The strength and mobility of the ball joint are measured using specialized testing equipment. These tests determine whether the ball joint is functioning properly and if there is any wear.
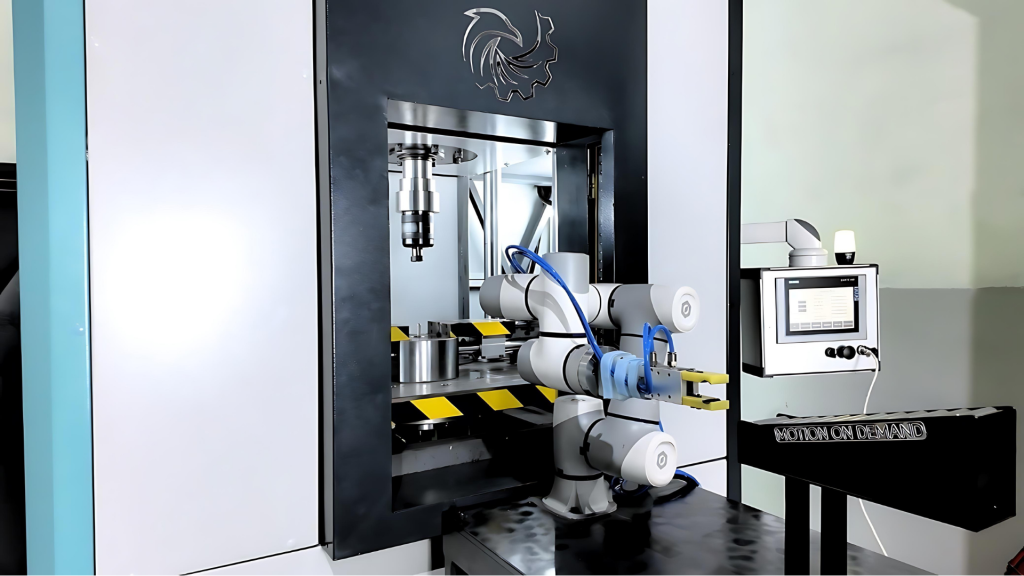
Conducting these tests regularly and performing the necessary maintenance and repairs based on the results is crucial for preventing control arm failures and ensuring vehicle safety. During the manufacturing phase, both industrial and customer-specific tests are applied. These tests are conducted using static tensile/compression testing machines and fatigue testing machines on Dynaress test machines. These systems, designed to meet your needs, are produced and offered by us. For more detailed information, please visit our website.



